BIOEQUIVALENCE STUDY
The process of research and development of a new pharmaceutical is very time-consuming, extremely expensive. A new drug will be approved for market, this process can take 10 to 15 years and cost millions of dollars. Therefore, after researching a drug successfully, the manufacturer has drug patent and most drug patents are protected up to 20 years. A drug is first made is called an (Innovator Pharmaceutical Product), and this drug is allowed to be marketed under the (Trade Name)
The trade name drugs are often expensive, during the patent period (20 years) other companies can not make or sell the same drug until the patent expires. For that reason, not at all people in the world have access to medicines, especially people in poor and developing countries.
When the patent expires anyone is free to manufacture and sell what is now termed a generic pharmaceutical.
With the explosion of the pharmaceutical industry, with hundreds even thousands of different pharmaceutical companies all over the world. Only one an originalbrand name drug after the patent expires may be available hundreds, thousands of new brand name drugs with the same generic name.
How to make sure that the generic drug is the same as a brand name drug in quality?
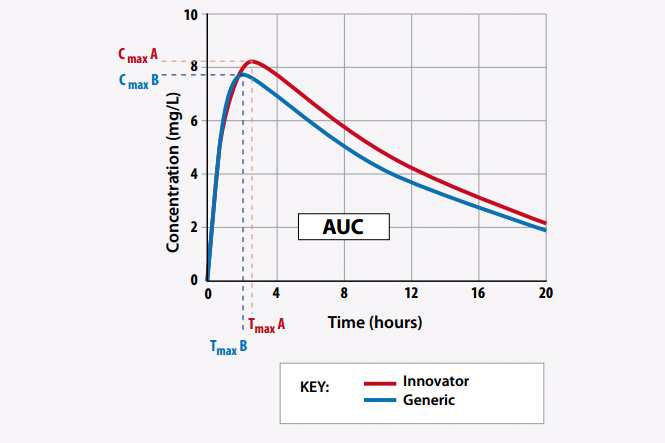
BIOEQUIVALENCE IS THE KEY TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION.
Bioequivalence means the equivalence of bioavailability between two drugs under the same conditions (Law on pharmacy, 2016). In other words, two drugs are considered as bioequivalence if they are pharmaceutical equivalence drugs or pharmaceutical alternatives and their bioavailability after taking the same dose in the same conditions of the test is similar so their treatment effect is considered to be basically equivalent to each other. (Circular No.08/2010/TT-BYT).
Bioequivalence studies are conducted under serious and tight regulation. This regulation has been the consensus in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations with reference to the regulations of the European Medicines Agency and the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In the bioequivalence study, there are two most important phases, the clinical phase (they are related to human aspects) and the biological fluid analysis phase (which is the phase related to the technical process and the accuracy of the study). Both of these two phases must be performed in qualified research centers (GCP standard: Good clinical practice for human studies phase; and GLP standard: Good laboratory practice for the biological fluid analysis phase).
THE RESULT OF THE BIOEQUIVALENCE TESTING ARE VERY IMPORTANT ROLE:
- Provide evidence about average bioequivalence in drug absorption of test drug compared to reference drug, indicating indirectly the interchangeability of them in treatment (equivalent treatment).
- As premises licensing for circulating drug (for some drugs are required to test the equivalent of biology)
- Helping the business to develop the product, brand settings and fair competition.
- Building technical barriers in glocal and regional economic integration.
- Help to ensure equity and benefits for patients in treatment.